|
Location Registration and Recognition (LRR)
for Longitudinal Evaluation of Corresponding Regions in CT Volumes
This page gives a high level overview of our research on Location Registration and Recognition (LRR).
For more details, please refer to our article
published in MICCAI 2008 proceedings.
Contents
Overview
The algorithm described in this paper takes (a) two temporally separated
CT scans, 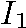 and and 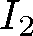 ,
and (b) a series of locations in ,
and (b) a series of locations in 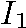 , and
it produces, for each location, an affine transformation mapping the locations
and their immediate neighborhood from , and
it produces, for each location, an affine transformation mapping the locations
and their immediate neighborhood from 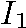 to to 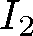 . It does this
without deformable registration by using a combination of feature extraction,
indexing, refinement and decision processes. Together these essentially
"recognize" the neighborhoods. We show on lung CT scans that
this works at near interactive speeds, and is at least as accurate as the
Diffeomorphic Demons algorithm [1]. The algorithm may be used both
for diagnosis and treatment monitoring. . It does this
without deformable registration by using a combination of feature extraction,
indexing, refinement and decision processes. Together these essentially
"recognize" the neighborhoods. We show on lung CT scans that
this works at near interactive speeds, and is at least as accurate as the
Diffeomorphic Demons algorithm [1]. The algorithm may be used both
for diagnosis and treatment monitoring.
Motivation and Intuition
-
| Given: | image volumes  and and
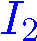 |
|
set of locations 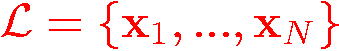 from from  . . |
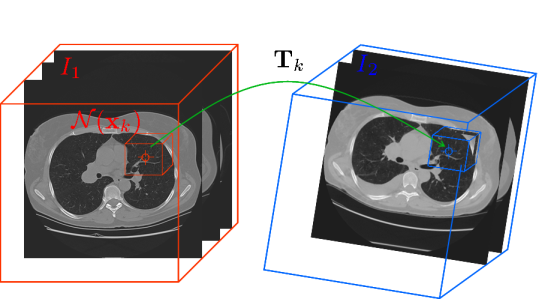
- Goal: find, for each
 ,
the affine transformation ,
the affine transformation 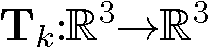 ,
which best aligns neighborhood ,
which best aligns neighborhood 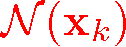 with a region of
with a region of 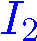 . .
Algorithm Outline
Results
Summary
- Algorithm for Location Registration and Recognition (LRR) without solving deformable registration first or simultaneously
- Technique to obtain initial transform using shape contexts
- Novel verification algorithm
- Handle changes within the local regions
- At least as accurate as the deformable registration
- Fast algorithm runs at near interactive speeds
Future work:
- Combining results from multiple locations, exploring other applications
Publications and Further Reading
Bibliography
[1]
Vercauteren, T., Pennec, X., Perchant, A., Ayache, N.: Non-parametric diffeomorphic
image registration with the demons algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 10th
International Conference of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted
Intervention (MICCAI 2007), Brisbane, Australia (2007) 319-326.
|